
12/05/2021VAT
Value-added tax (VAT) is levied on goods and services in the UK. It is a type of consumption tax, as it is levied on the items and services that people use in their daily lives. It is an indirect tax that government collects by businesses. In this blog, we’re going to discuss the UK value added tax rate.
Remove your VAT troubles with CruseBurke!
Value Added Tax Rate:
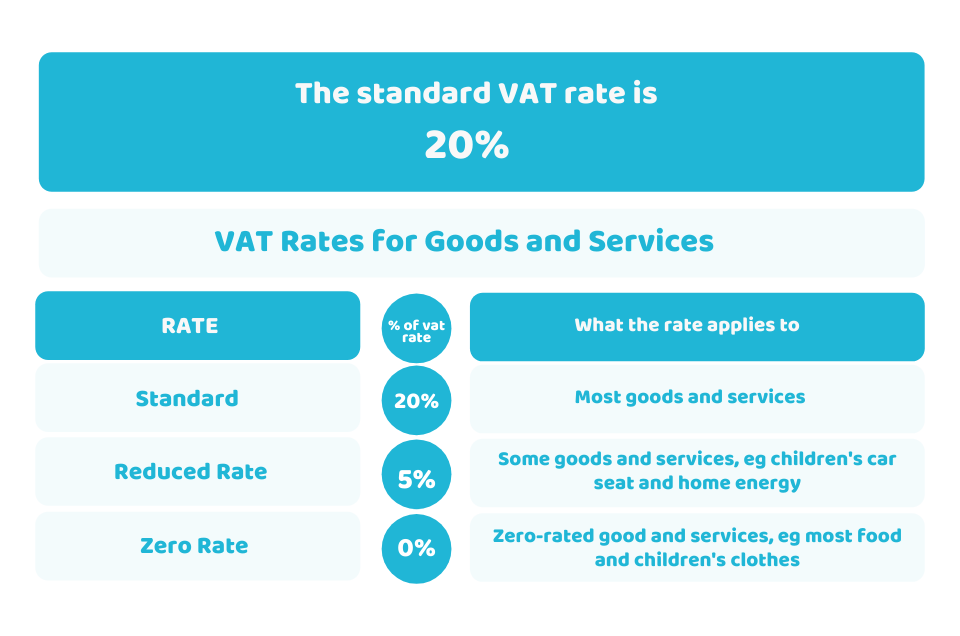
On most purchases, the standard UK value added tax rate is 20%. However, there’re also other tax rates including a 5% reduced rate on energy-saving measures, children’s car seats and sanitary products.
The zero rates are applied on most books, newspapers, foods and children’s clothes. You don’t need to pay VAT on these items. But you have to record and report it to your VAT returns.
Some items are exempted from VAT, like financial or property transactions and postal stamps.
According to EU law, the standard rates of VAT in EU states ought to be 15% or more.
Key Takeaway: After Income Tax and National Insurance contributions, VAT is the third biggest source of revenue for the UK government.
Get connected with our VAT Accountants!
Who’s Liable to Pay VAT?
If your business has annual revenue above £85,000, you are obliged to register to pay and charge VAT on the products and services you buy or sell. In case you are earning below this threshold, you can voluntarily register and pay VAT. Businesses charge VAT from the customers and then pay it to HMRC while filing their VAT returns.
How can You Pay VAT?
HMRC accepts the VAT payment in various ways, the payment can be made on the same day or the next day:
- By Fast-payments via phone or online
- Through CHAPS using an online form
Along with the above ones, there are multiple payment options that will approximately take 3 to 5 working days to pay VAT:
- Direct debit
- At a bank or building society
- BACS
- Debit or credit card
- Standing order (for some VAT schemes)
Visit the government website to know how to pay your VAT bill Or ask us to do it.
How to Charge VAT?
You need to charge VAT along with the products and services you sell to your customers. You should add it to the amount you charge for product or services. You need to do it properly so that you’ll file accurate VAT returns and pay the money that you owe to HMRC.
The invoices need to have:
- The invoice number and date
- The details of your business including name, address etc
- The VAT registration number
- The customer’s details
- A description of the goods and services covered
You should clearly write the details of each in your invoice including:
- Unit price without adding VAT
- Quantity or weight
- VAT rate
- The total amount without paying VAT
- The VAT amount to pay
- Cash discount if any
Need Help with VAT:
Now, you have got enough information about the value-added tax rate. If you’re looking for expert assistance, CruseBurke has a team of certified VAT accountants for your help.
Feel free to leave your query here, we’ll get back to you soon.
Disclaimer: This blog provides general information on VAT.



